Quantum Computing
Welcome To
Resource Hub
Quantum Computing
The Next Frontier:
Quantum Computing

Where Classical Computing Meets Quantum Possibility
–
As we approach the limits of classical computing, quantum computers promise breakthroughs in:
- Drug discovery and materials science
- Financial modeling and optimization
- Climate simulation and prediction
- Cryptography and security
- Machine learning and AI
Our resource hub helps you understand:
- Core quantum computing concepts
- Key industry players and developments
- Investment opportunities
- Future implications and timeline
- Strategic considerations for business

Share This Class:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHOmBV4js_E
Overview
Unleashing the Power of Quantum Mechanics for Intelligent Systems
The intersection of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Quantum Computing represents a groundbreaking frontier in the development of intelligent systems. Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform complex computations that are intractable for classical computers. By leveraging the exponential computational power of quantum systems, AI algorithms can tackle problems of unprecedented scale and complexity, opening up new possibilities for machine learning, optimization, and simulation. Quantum AI has the potential to revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, financial modeling, and cryptography, by enabling the development of more sophisticated and efficient algorithms for pattern recognition, data analysis, and decision-making.
The integration of AI and quantum computing is still in its early stages, with researchers and industry leaders exploring the theoretical foundations and practical applications of this emerging field. Quantum machine learning algorithms, such as quantum neural networks and quantum support vector machines, are being developed to exploit the unique properties of quantum systems for enhanced performance and generalization. Quantum-inspired optimization algorithms, such as quantum annealing and quantum approximate optimization algorithms (QAOA), are being applied to complex problems in logistics, scheduling, and resource allocation. Additionally, quantum AI is being used to develop more realistic and accurate simulations of quantum systems, with applications in materials science, chemistry, and beyond. As quantum hardware continues to advance and scale, the potential impact of quantum AI on industry and society is immense. However, significant challenges remain, including the development of robust and scalable quantum algorithms, the integration of quantum and classical computing frameworks, and the need for interdisciplinary collaboration between AI researchers, quantum physicists, and domain experts.
FAQ’s
What is quantum computing, and how does it differ from classical computing?
Quantum computing is a type of computing that uses quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. Unlike classical computers, which use bits that can be either 0 or 1, quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits) that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This allows quantum computers to solve certain complex problems much faster than classical computers.
What are the potential applications of quantum computing in AI?
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize AI by enabling faster and more efficient processing of large datasets, optimizing machine learning algorithms, and solving complex optimization problems. Some potential applications include:
- Quantum neural networks for improved pattern recognition and classification
- Quantum-enhanced deep learning for more accurate and efficient training
- Quantum algorithms for faster search and optimization in AI problems
- Quantum-powered natural language processing and sentiment analysis
How can quantum computing accelerate machine learning?
Quantum computing can accelerate machine learning by leveraging quantum algorithms for faster linear algebra operations, which are the backbone of many machine learning models. Quantum computers can also efficiently process and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling more complex and accurate models. Additionally, quantum computing can help with feature selection, dimensionality reduction, and optimization tasks in machine learning.
hat are some examples of quantum algorithms used in AI?
Some examples of quantum algorithms used in AI include:
- Quantum Support Vector Machines (QSVM) for classification tasks
- Quantum Principal Component Analysis (QPCA) for dimensionality reduction
- Quantum Boltzmann Machines (QBM) for unsupervised learning and generative models
- Quantum Gradient Descent (QGD) for optimization and training of AI models
- Quantum Reinforcement Learning (QRL) for sequential decision-making problems
What are the challenges and limitations of quantum computing in AI?
Some challenges and limitations of quantum computing in AI include:
- Scalability: Building and maintaining large-scale, stable quantum computers is still a significant challenge.
- Error correction: Quantum systems are highly sensitive to noise and errors, requiring robust error correction techniques.
- Algorithm development: Designing and implementing efficient quantum algorithms for AI tasks is an ongoing research area.
- Integration: Integrating quantum computing with classical AI systems and workflows requires new software and hardware architectures.
- Skills gap: There is a shortage of quantum computing experts and AI professionals with quantum programming skills.
What are some current research areas in quantum AI? A: Some current research areas in quantum AI include:
- Quantum machine learning algorithms and frameworks
- Quantum neural networks and deep learning architectures
- Quantum natural language processing and sentiment analysis
- Quantum computer vision and image recognition
- Quantum-enhanced reinforcement learning and decision-making
- Quantum generative models and unsupervised learning
- Quantum-classical hybrid AI systems and algorithms
What are some companies and organizations working on quantum AI?
Some companies and organizations working on quantum AI include:
- Google AI Quantum: Developing quantum algorithms and software for machine learning
- IBM Quantum: Building quantum hardware and software for AI and other applications
- Microsoft Quantum: Creating quantum development tools and algorithms for AI
- Amazon Braket: Providing cloud-based quantum computing services for AI and other use cases
- Xanadu: Developing quantum software and algorithms for machine learning and optimization
- QCWare: Offering quantum computing software and services for AI and other industries
How can I learn more about quantum computing and its applications in AI?
To learn more about quantum computing and its applications in AI, you can:
- Take online courses and tutorials on quantum computing and quantum machine learning (e.g., on Coursera, edX, or Qiskit)
- Read research papers and articles on quantum AI from conferences and journals (e.g., NIPS, IEEE, Nature)
- Join quantum computing and AI communities and forums (e.g., Quantum Computing Stack Exchange, Quantum AI Lab)
- Attend workshops, webinars, and conferences on quantum AI (e.g., QML, Q2B, IEEE Quantum Week)
- Experiment with quantum computing and AI libraries and frameworks (e.g., PennyLane, TensorFlow Quantum, Qiskit ML)
Featured Courses & Case Studies
Upcoming Events



Quantum Computing
Quantum computing utilizes quantum mechanical phenomena like superposition and entanglement to perform computations. It relies on qubits which can exist in a combination of 1 and 0 states simultaneously. This enables quantum computers to encode much more information and process it in parallel compared to classical binary bits. Leading to exponential speedups for specialized algorithms like integer factorization used in cryptography and machine learning. However, quantum computing hardware is extremely fragile and scaling remains challenging. Companies like IBM, Google, Rigetti and IonQ are at the forefront – building and providing access to early quantum systems with 10-100 qubits for research purposes.
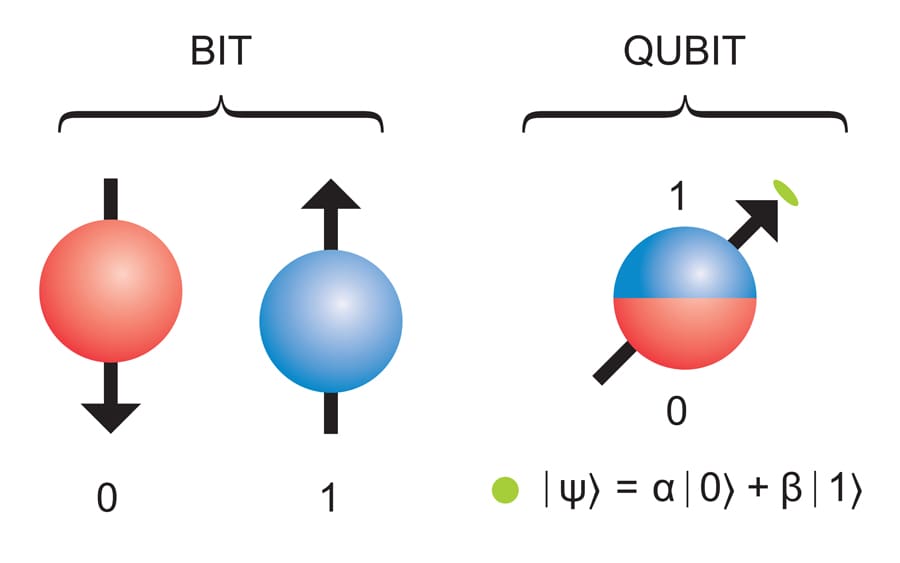
Qubit
A qubit, or quantum bit, is the basic unit of information in quantum computing. Unlike classical binary bits that can only be in a state of 0 or 1, qubits can exist in a superposition of both 0 and 1 simultaneously due to quantum mechanical effects. This enables a qubit to essentially encode more information and process it in parallel, allowing quantum computers to theoretically solve certain problems exponentially faster. However, this superposition is very delicate and easily disrupted through interference from the external environment. Maintaining and controlling the quantum state of qubits is extremely complex, requiring advanced hardware like cryogenic refrigerators to keep qubits near absolute zero. The development of stable, scalable qubits is one of the main challenges towards realizing practical quantum computers.
Calculations
Quantum calculations utilize the key principles of quantum mechanics – superposition, entanglement, and interference – to perform computations. Qubits can represent a combination of 1 and 0 states, allowing quantum algorithms to encode information densely via superposition and process it in parallel. This parallelism enables exponential speedups compared to classical computations for specialized problems like factoring large numbers and optimization tasks. However, quantum states are fragile and prone to errors from environmental noise and interference. Quantum circuits model algorithms using a series of quantum logic gates that manipulate qubit states precisely to maintain coherence and quantum parallelism through the calculation process. Current quantum hardware uses techniques like quantum error correction and fault tolerance to enable accurate calculations on a small scale.
Algorithms
Quantum algorithms are designed to harness the unique capabilities of quantum computing to solve problems faster than classical methods. They take advantage of quantum mechanical phenomena like superposition and entanglement to process information in parallel. Algorithms like Shor’s factor large numbers exponentially faster, while Grover’s algorithm speeds up search in unsorted databases. Quantum machine learning algorithms use quantum data encoding and interference to detect patterns in large data more efficiently. Quantum simulation replicates quantum systems on quantum hardware for insights into chemistry, materials and more. However, identifying applications which demonstrate quantum advantage over classical hardware remains an active area of research. Current quantum algorithms show great promise, yet success depends largely on overcoming hardware-imposed limits on scale and error correction as quantum systems progress towards practical applications.

Quantum Teleportations
Quantum teleportation is a process where quantum information can be transmitted from one location to another without having to physically travel through the intervening space. It relies on the quantum mechanical phenomena of entanglement to establish a connection between two particles over any distance. By making a measurement of the entangled pair, the quantum state of one particle can be instantaneously transferred to another, destroying the original in the process. This allows teleporting the qubit state in quantum computers and networks. However, only the quantum information is teleported this way, not the physical matter. While theoretically promising for achieving long-distance quantum communication, the fragility of entangled states makes scaling up teleportation technologically challenging. Advances in optical links and matter-based quantum repeaters provide promising routes towards usable quantum teleportation.